Keyboard ALT + g to toggle grid overlay
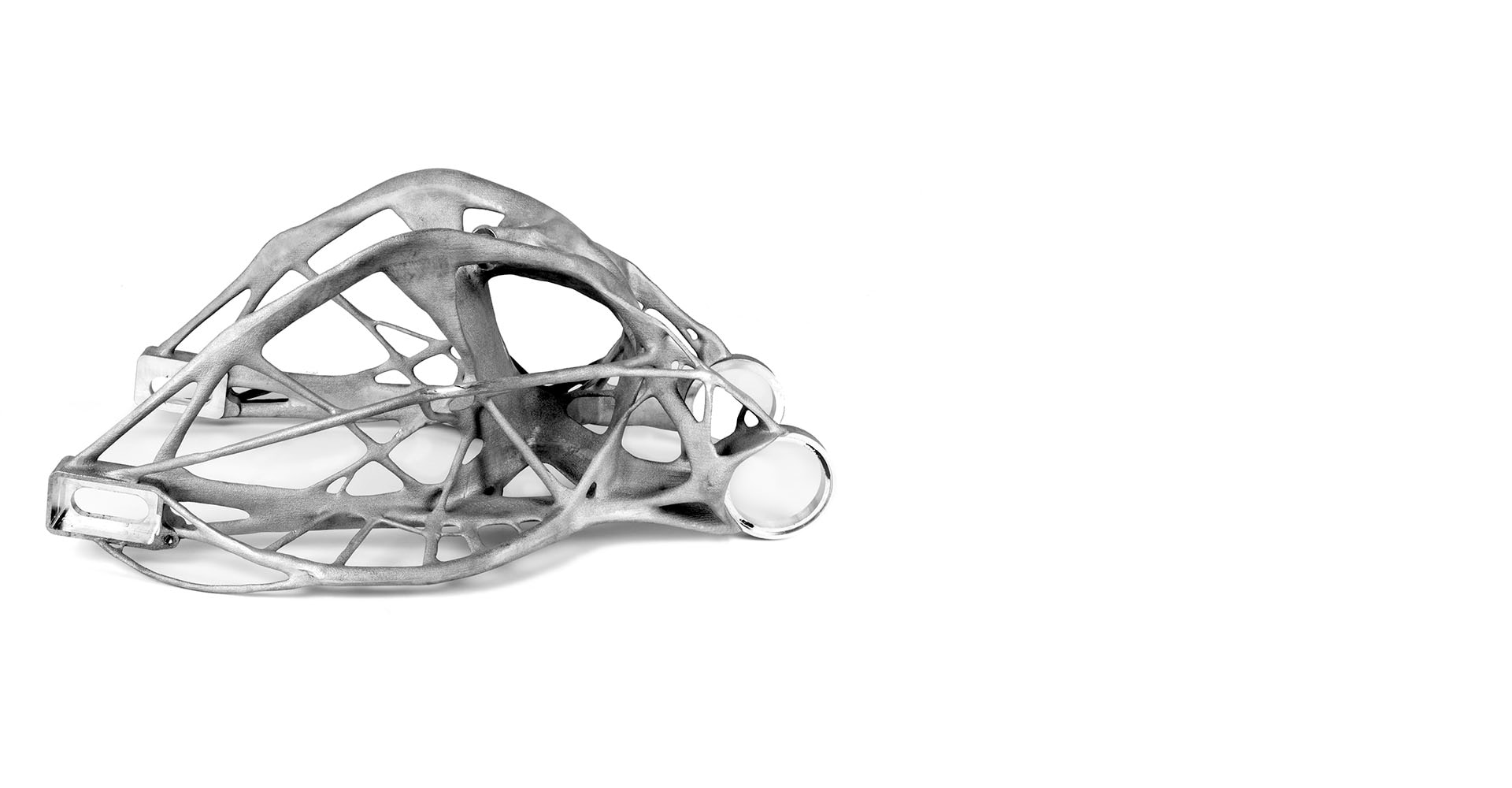


What is additive manufacturing?
Additive manufacturing, also known as 3D printing, is a process used to create a physical (or 3D) object by layering materials one by one based on a digital model. Unlike subtractive manufacturing that creates its final product by cutting away from a block of material, additive manufacture adds parts to form its final product.
Types of additive manufacturing
Additive manufacturing can encompass multiple processes, depending on the hardware, material requirements and product application.
-

VAT PHOTOPOLYMERISATION
A vat of photopolymer liquid is cured by focused UV light that builds parts layer by layer for a high-detail surface finish.
-

BINDER JETTING
A power substrate is hardened when the printing head deposits a drop of binding fluid in a layering process. Includes full-colour prototype fabrication.
-

MATERIAL JETTING
Primarily used where surface finished and form testing are needed; a printhead lays down successively solidifying layers of UV curable material to form prototyped designs.
-

MATERIAL EXTRUSION
Fused deposition modelling is a common 3D printing process in which a heated nozzle extrudes a plasticised material to form products from a sliced CAD model.
-

POWDER BED FUSION
Laser or electron beams quickly fuse layered powder material, such as various metals, together. Used for circuits, structures and parts.
-

SHEET LAMINATION
Ribbons of metal or paper are bonded through ultrasonic welding or adhesive, respectively; the finished shaping is completed through further material removal processes.
-

DIRECTED ENERGY DEPOSITION
Repairs or adds to existing components by using a multi-axis nozzle to extrude laser-melted material, commonly metal powders, onto the printing surface.
-

METAL CASTING
Using generative design and simulation software to produce complex metal parts helps manufacturers get more value from proven metal casting processes.
How is additive manufacturing used today?

LIGHTWEIGHT COMPONENTS
One of the earliest ways to use additive manufacturing for industrial purposes, this practice is now becoming an industry standard. CAD-to-additive simulation technology is improving exponentially.

CUSTOMISED TAILORED COMPONENTS
Additive engineering provides the flexibility that manufacturers need to deliver customised solutions to clients quickly.

ON-DEMAND PRODUCTION
Prototyping is the original use of additive manufacturing. Though it is still widely used for that purpose, many companies succeed in delivering reliable 3D-printed finished goods.
The additive manufacturing ecosystem
-
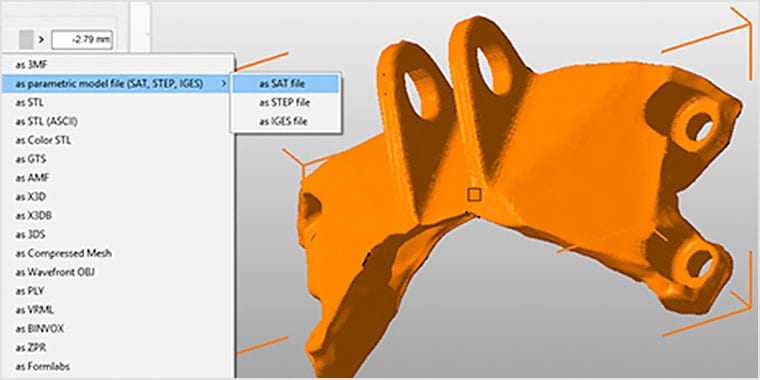
SOFTWARE
Additive fabrication would not be possible without the high-calibre software required to prepare CAD geometry for printing.
-

HARDWARE
Autodesk has partnerships and integrations with dozens of leading hardware manufacturers.
-

MATERIALS
Materials science is at the forefront of the industry, providing novel ways to work with everything from existing plastics to futuristic alloys.
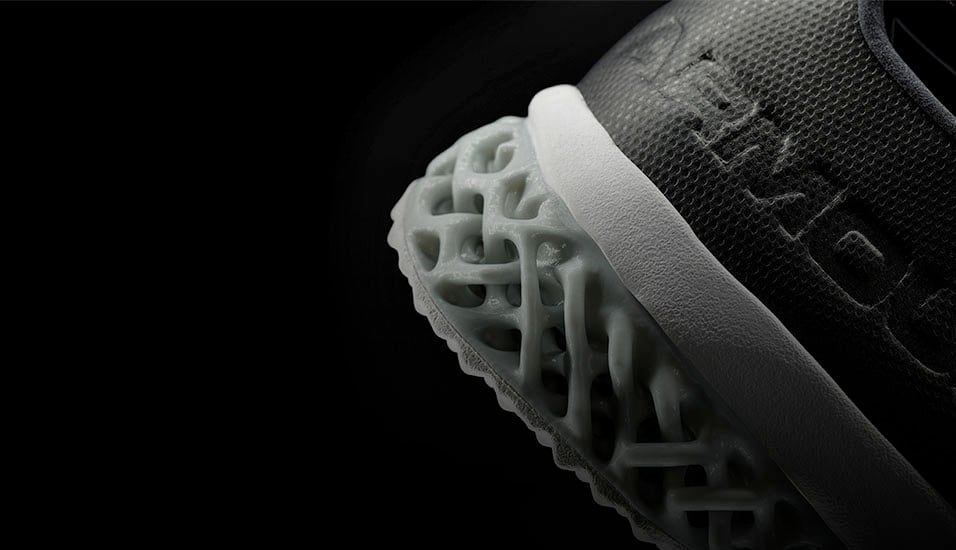




How to design for additive manufacturing
Additive engineering is evolving at a fast pace. 3D printing now involves metal laser sintering, powder bed fusion and even hybrid techniques involving casting and robotics.

Trends in additive manufacturing
Additive manufacturing has evolved rapidly in recent years. It has been embraced by major industrial companies looking for ways to improve their products. The ability to deliver near-instant parts production and fully customised designs that cannot be replicated with other manufacturing techniques has accelerated investment and research in additive engineering.
Examples of additive fabrication trends
-
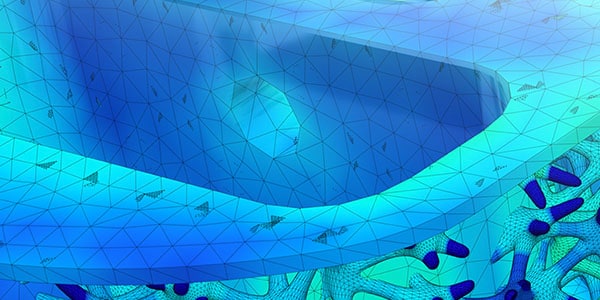
SIMULATION
With metal additive manufacturing, materials are expensive and lead times are compressed. Consultants, innovation labs and researchers are turning to process simulation to minimise 3D printing failures.
Discover Netfabb simulation capabilities (US Site)
-

ROBOTICS
Robots are capable of incredible manufacturing feats, and their use in various fields is advancing rapidly, such as programmable multi-axis capabilities combined with computer vision research to build bridges.
-

GENERATIVE DESIGN
Quickly generate multiple high-performing, CAD-ready designs from a single idea. Get thousands of solutions from one idea and choose the one that suits your needs.
Learn more (US Site)
-

HYBRID MANUFACTURING
Metal additive fabrication often requires subtractive CNC finishing. Success with hybrid processes requires planning during the design phase and accommodations in the additive manufacturing phase.
Featured software for additive manufacturing
Free additive manufacturing software and guide
FREE SOFTWARE FOR STUDENTS AND EDUCATORS
Fusion 360 free 3D CAD/CAM design software for students, educators and academic institutions.
THE DEFINITIVE GUIDE TO DESIGNING FOR ADDITIVE MANUFACTURING
Get the engineer’s guide to understanding and implementing additive manufacturing in the production process.
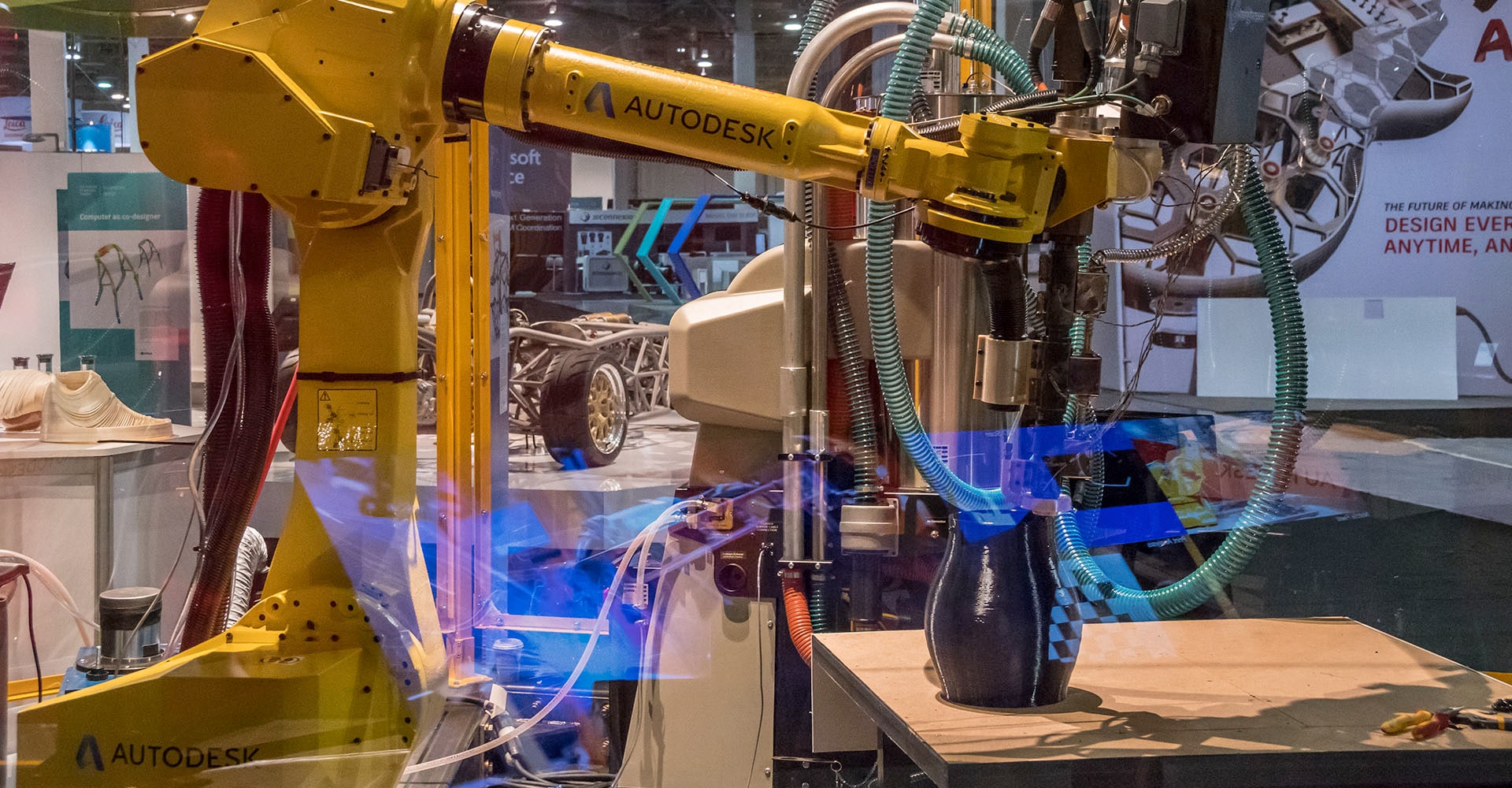
Research and development
From 3D printed houses to additive technology that works in space, additive is the future of manufacturing.
Additional resources for additive manufacturing
Read about additive manufacturing trends and future materials.
-
The first 3D-printed ship’s propeller project, based out of the Port of Rotterdam’s RAMLAB facility passes seafaring test.
-
NASA’s Swamp Works lab is experimenting with 3D-printing habitable structures using a process called robotic extrusion and a composite material made up of loose sediment.
-
Lower-cost, safer processes are replacing old ways of doing things.
-
To push the boundaries on its next generation of lightweighting, the car manufacturer is looking to Autodesk technologies to develop future cars and trucks.
-
New specification maximises potential for efficient and lightweight additive manufacturing design.
-
Thrashing the future of design (US Site)
Similar to aircraft parts, furniture and many more modern objects, skateboard trucks are set to change, thanks to topology optimisation and metal additive manufacturing.