& Construction

Integrated BIM tools, including Revit, AutoCAD, and Civil 3D
& Manufacturing

Professional CAD/CAM tools built on Inventor and AutoCAD
Use Loop blocks to iterate, or loop, through logic statements in the Informed Design Codeblocks Rule Editor.
Loop code blocks provide a way to control how many times a block body is run. Loops indicate that the body of the code block is repeated, or looped through, multiple times. An iteration is a pass through a single loop.
The simplest Repeat block runs the code in its body the specified number of times.
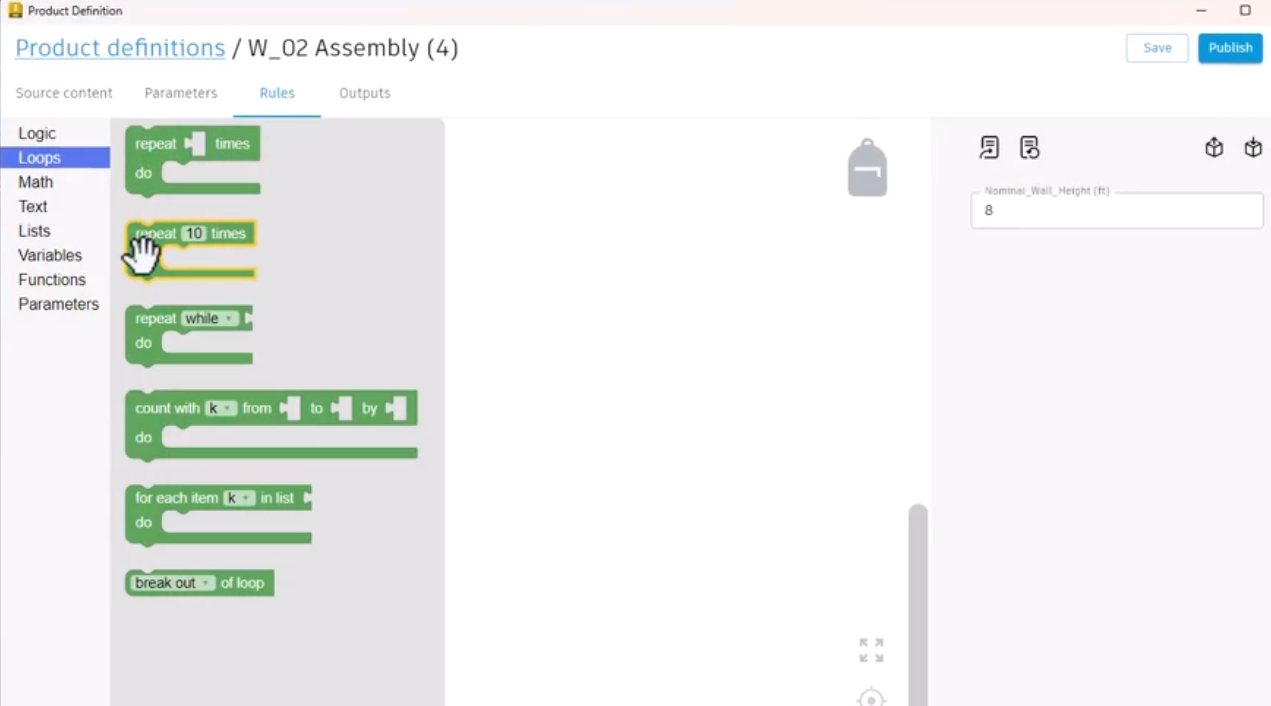
The specified text is printed three times.

Use a Math block in conjunction with a Repeat block to calculate the number of iterations through a loop.

The block calculates the number of times to print by subtracting 4 from the Nominal Wall Height value. In this case, the text is printed 4 times.
The Loop block automatically runs, recalculates the number of loops, and prints the text 6 times.
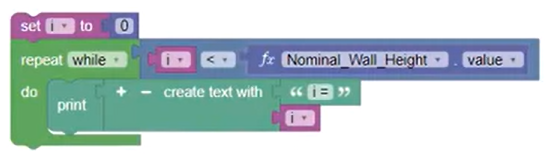
Use the Repeat While Loop block to iterate over a code block as long as a specific condition is true.
An infinite loop error displays, because the While condition never terminated to end the loop.
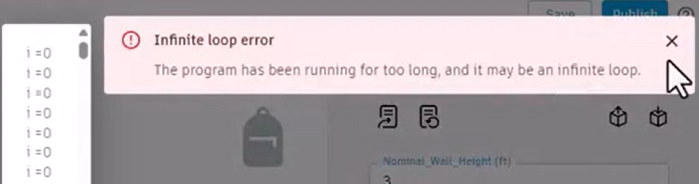
To resolve the error:
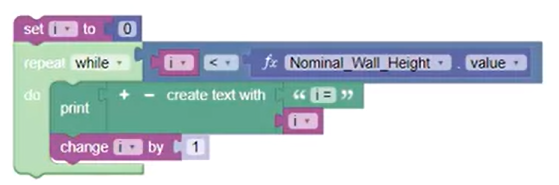
The loop advances the value of i by 1 for each iteration, but only while i is less than the parameter value. For example, with a Nominal Wall Height value of 4, the value of i is printed from 0 to 3.

Repeat Until loops are like While loops, but they repeat until the condition is true, and then they stop looping.
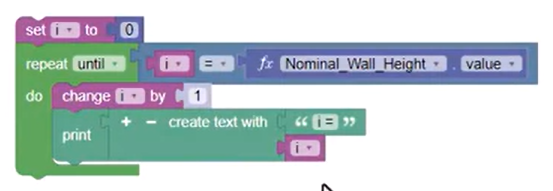
The code block runs until the i variable equals the value of the Nominal Wall Height parameter.
The Count With block iterates a variable from one value to another value by a specified increment amount, looping once for each step.
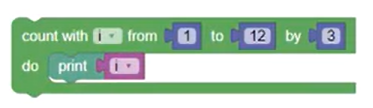
Because the increment is set to 3, the next increment after 10 is 13, so 10 is the last number printed.

The For Each block iterates over the values in a list. Rather than stating loop x many times, the For Each block states loop through every item in a set of values.
Note that attaching the block straight from the Parameters library is not allowed, because the For Each block expects a list and not a single value.
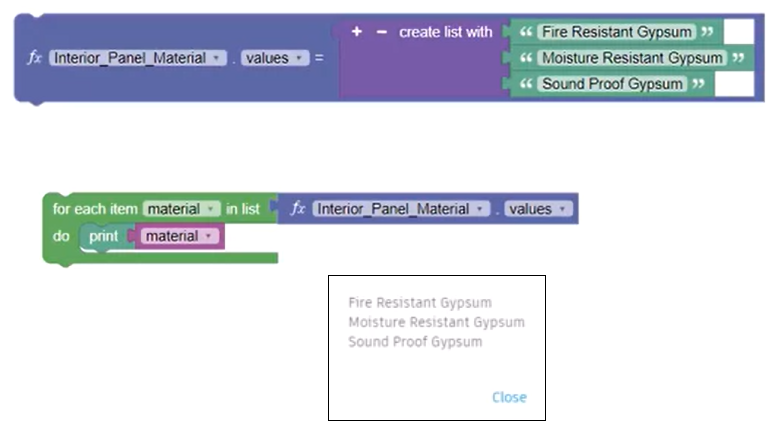
Most loops run until a terminating condition is reached, or until all values have been looped through. Use a Loop Termination block to exit, or break, from a loop.
In this example, the Loop Termination block is placed in the Do portion of the For Each If Do statement and is set to break out of the loop if the list encounters “High Impact Gypsum”.
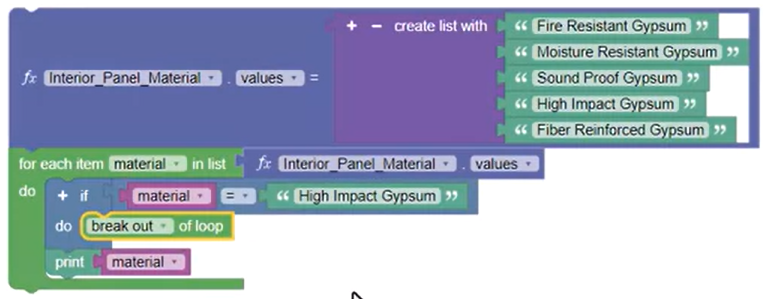
The Loop Termination block can be set to skip printing the specified material.
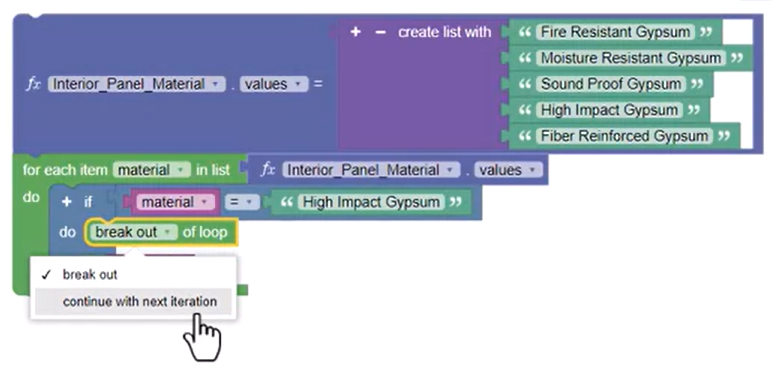
Now, running the For Each block prints all the materials in the list except High Impact Gypsum.
In summary, loop blocks provide a way for logic to efficiently run multiple times. Repeat loops allow a block to loop while, or until, a condition is met. Count With blocks loop from one number to another by a specified increment. For Each loops iterate through values in a list. Loop Termination blocks exit a block or skip an iteration when a condition is met.