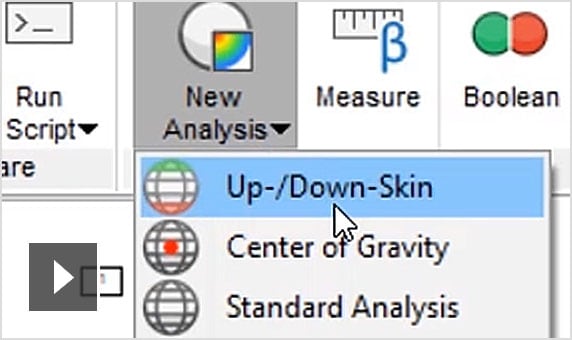
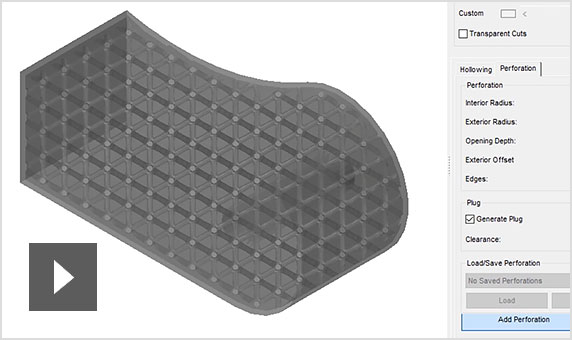
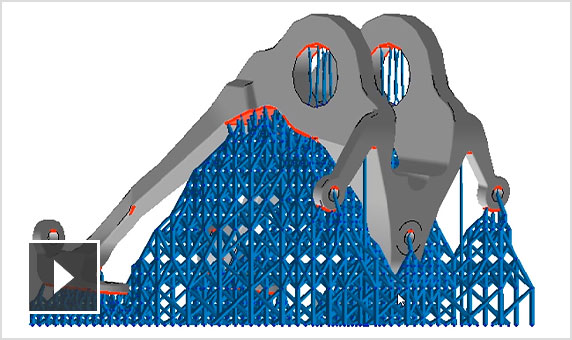
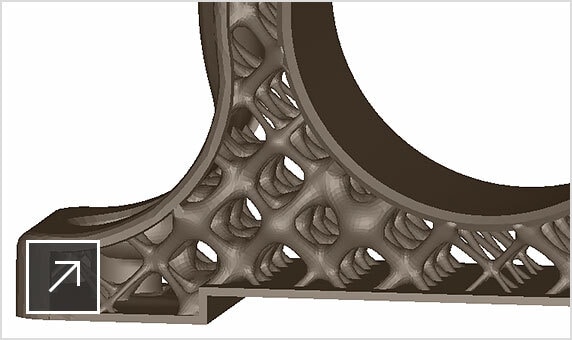
Netfabb Premium
adsk-otfdl-mobile-user-heading
adsk-otfdl-mobile-user-text
adsk-otfdl-mobile-email-sent-text
adsk-oxygen-trial-download-product-selection-heading
adsk-oxygen-trial-download-product-selection-text
adsk-oxygen-trial-flow-introductory-header
adsk-oxygen-trial-flow-available-platforms-header
adsk-oxygen-trial-flow-systems-requirements-text
adsk-oxygen-trial-flow-trial-file-size-header
2 adsk-oxygen-trial-flow-filesize-units-gigabytes
adsk-oxygen-trial-flow-recommended-section-header
adsk-oxygen-trial-flow-recommended-section-text
adsk-oxygen-trial-flow-user-lang-os-intro-header
adsk-oxygen-trial-flow-user-type-intro-text
adsk-oxygen-trial-flow-business-heading
adsk-oxygen-trial-flow-business-text
adsk-oxygen-flow-user-os-selection-single
adsk-oxygen-flow-user-os-selection-multi
adsk-oxygen-flow-user-os-selection-error
adsk-oxygen-trial-flow-user-language-text
adsk-oxygen-trial-flow-edu-license-heading
adsk-oxygen-trial-flow-edu-license-text
adsk-oxygen-trial-flow-personal-user-license-heading
adsk-oxygen-trial-flow-personal-user-license-text
adsk-trial-phone-ver-title
adsk-trial-phone-ver-description
adsk-trial-phone-ver-number-label
adsk-trial-phone-ver-method
adsk-oxygen-trial-flow-voice-cta adsk-oxygen-trial-flow-text-ctaadsk-trial-phone-ver-code adsk-oxygen-trial-flow-resend-cta
trial-ph-ver-err-invalid-code
adsk-oxygen-trial-download-recaptcha
adsk-oxygen-trial-flow-dlm-text
adsk-oxygen-trial-flow-dlm-link-text
adsk-oxygen-trial-flow-dlm-link-text
adsk-otfdl-confirm-heading
adsk-otfdl-confirm-step-1
adsk-otfdl-confirm-step-2
adsk-otfdl-confirm-step-3