& Construction

Integrated BIM tools, including Revit, AutoCAD, and Civil 3D
& Manufacturing

Professional CAD/CAM tools built on Inventor and AutoCAD
Choose a template in Civil 3D, set up the coordinate system, set the project units, and define the surface.
Tutorial resources
These downloadable resources will be used to complete this tutorial:
When importing and exporting surface data between Civil 3D and InfoDrainage, it is very important to set up the coordinate system properly, to prevent problems with model objects and surfaces not lining up. The project units and the template also must be correct to ensure a smooth data exchange.
First, choose the template:
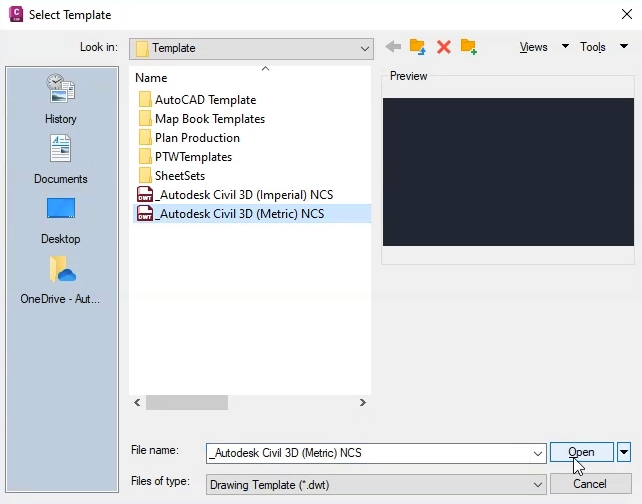
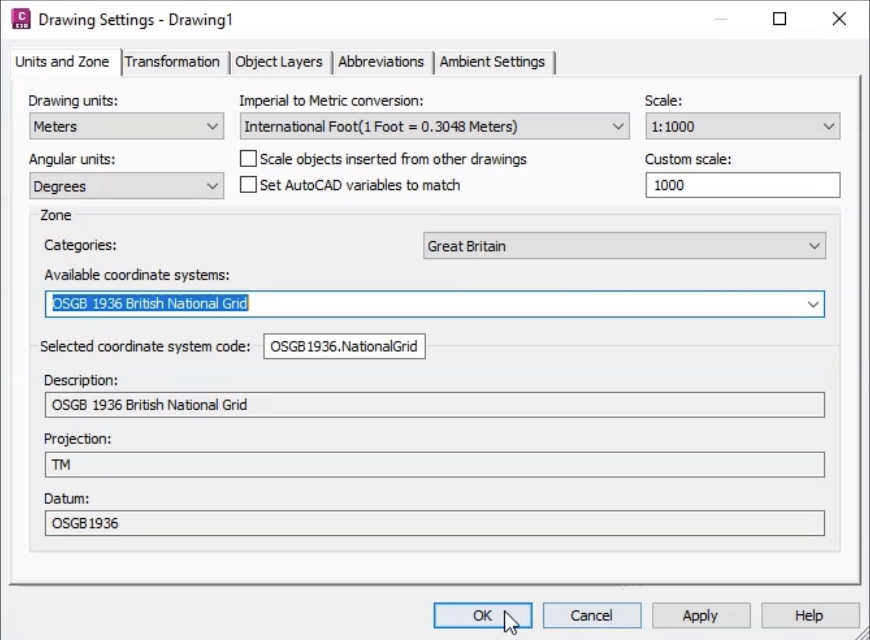
Next, set the categories and coordinate system according to your local standards. This example is located in the United Kingdom—specifically, Great Britian—so the settings used here are for the UK grid coordinate system:
Next, set up the surface data used to define manhole cover levels and pond perimeter levels.
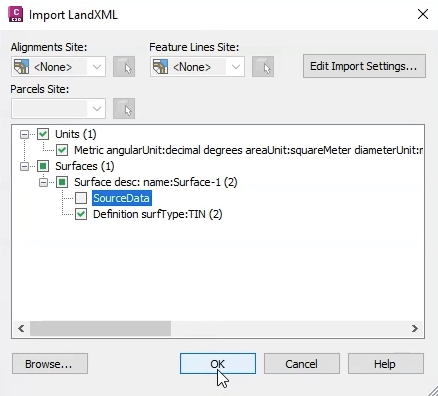
The surface model appears in the drawing window.
You could also add a description or edit the default styles, but for this exercise, leave them as-is.
The template, coordinate system, and surface file are now all configured.
IMPORTANT: For your local projects, you would configure these settings to match your local standards.